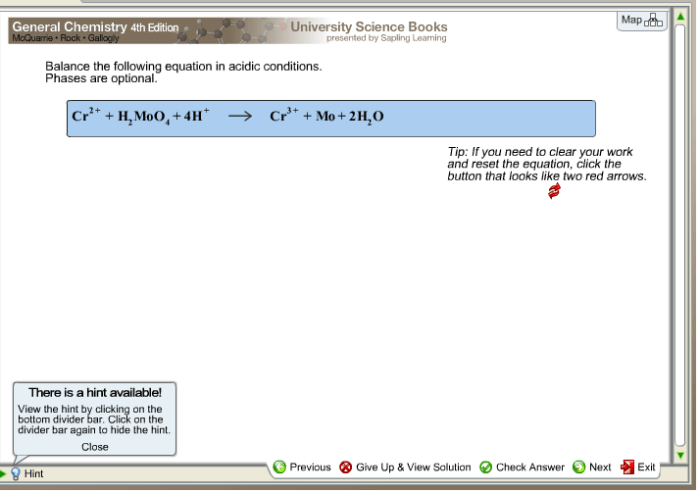
Balance the equation in acidic conditions phases are optional – Balancing chemical equations in acidic conditions presents unique considerations, with optional phases adding another layer of complexity. Understanding the principles and methods involved empowers chemists to accurately represent these reactions, unlocking a deeper comprehension of chemical processes.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of balancing equations in acidic conditions, exploring the concept, specific rules, and various methods employed. It also sheds light on the role of phases in balancing equations, providing a thorough understanding of this essential aspect of chemical reactions.
Chemical Equation Balancing in Acidic Conditions
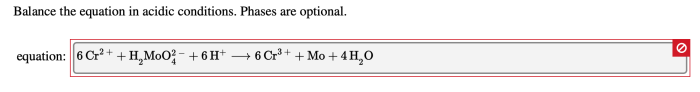
Balancing chemical equations is a crucial aspect of chemistry, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. In acidic conditions, specific rules apply to balance equations accurately.
When balancing equations in acidic conditions, it’s important to:
- Include hydrogen ions (H+) on the reactant side if the reaction occurs in an acidic solution.
- Balance the charge by adding electrons (e-) to the appropriate side of the equation.
- Use water molecules (H2O) to balance the oxygen atoms.
Phases of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions can occur in different phases, including:
- Solid (s)
- Liquid (l)
- Gas (g)
- Aqueous (aq) – dissolved in water
Phases play a crucial role in balancing equations, as they indicate the physical state of the reactants and products.
Methods for Balancing Equations, Balance the equation in acidic conditions phases are optional
Two common methods for balancing equations are:
Half-Reaction Method
Involves splitting the overall reaction into two half-reactions (oxidation and reduction) and balancing each half-reaction separately.
Oxidation Number Method
Assigns oxidation numbers to each element in the equation and adjusts the coefficients to ensure that the total change in oxidation numbers is zero.
Applications of Balanced Equations
Balanced equations are essential in chemistry for:
- Determining the stoichiometry of reactions
- Predicting the products of a reaction
- Calculating the amount of reactants or products needed or produced
General Inquiries: Balance The Equation In Acidic Conditions Phases Are Optional
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations?
Balanced chemical equations ensure that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side matches the number of atoms of the same element on the products’ side, providing an accurate representation of the chemical reaction.
How do phases affect the balancing of chemical equations?
Phases, such as solid, liquid, or gas, indicate the physical state of the reactants and products. They can influence the stoichiometry of the reaction and must be considered when balancing equations.
What is the difference between the half-reaction method and the oxidation number method for balancing equations?
The half-reaction method involves splitting the reaction into two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction. The oxidation number method assigns oxidation numbers to each element and uses these to determine the number of electrons transferred, aiding in balancing the equation.