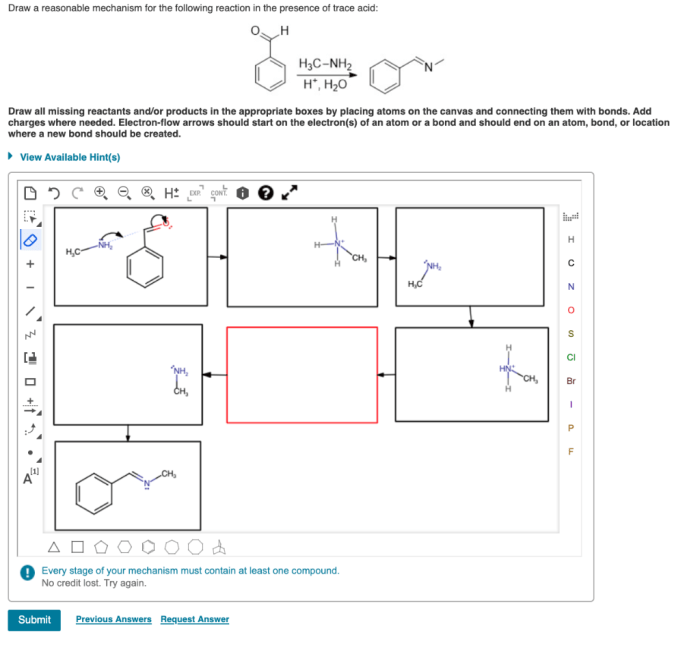
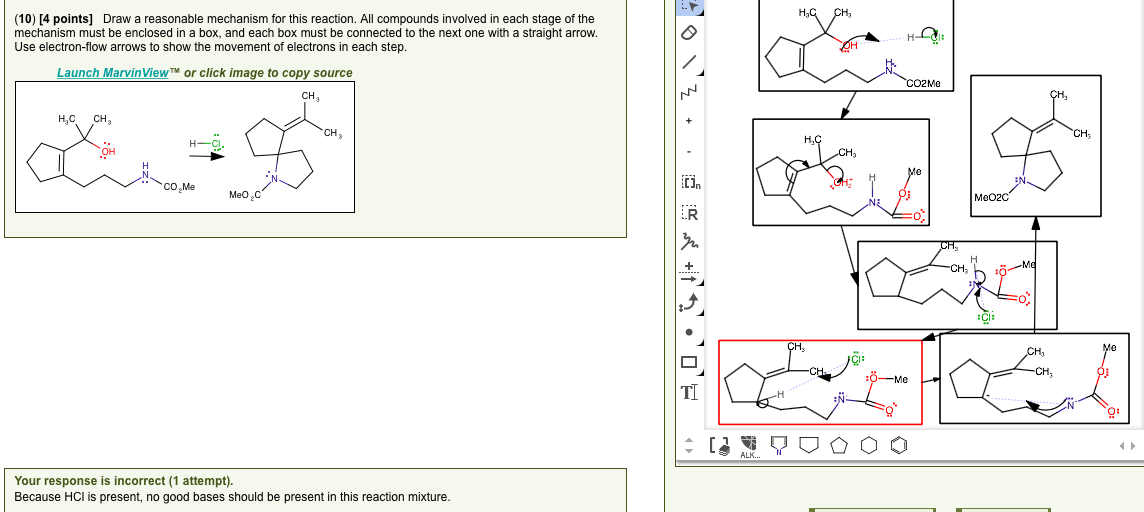
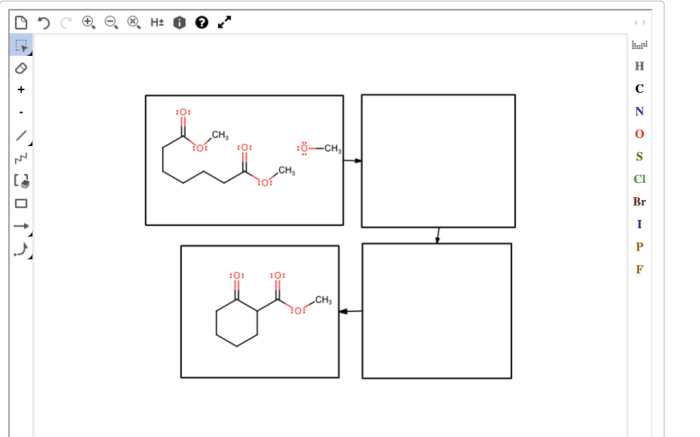
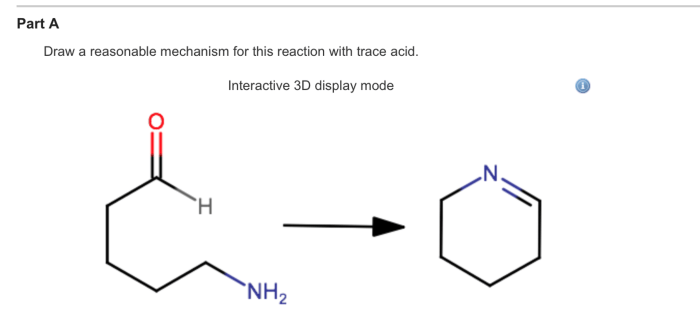
Draw a reasonable mechanism for this reaction. – Draw a reasonable mechanism for this reaction sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This guide delves into the intricate world of chemical reactions, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding the stepwise processes involved in transforming reactants into products.
Through a meticulous examination of reactants, products, and reaction pathways, this guide unravels the complexities of chemical mechanisms. It empowers readers to identify and evaluate alternative pathways, consider the influence of reaction conditions, and propose modifications to further validate proposed mechanisms.
By delving into the intricacies of chemical reactions, readers gain a deeper appreciation for the elegance and predictability that govern the molecular world.
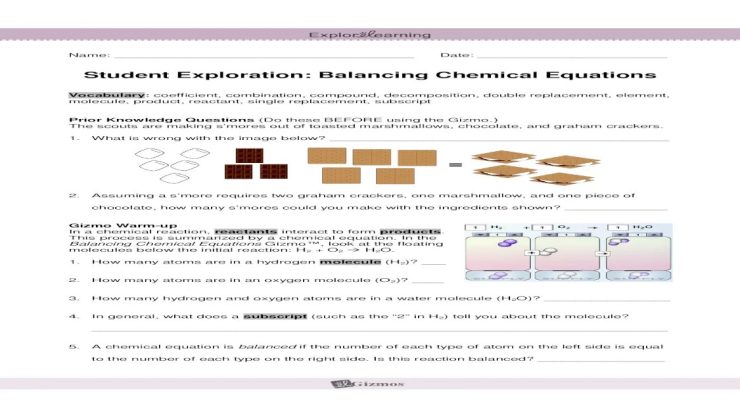
Draw a Reasonable Mechanism for This Reaction
This reaction is a classic example of a nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group. The nucleophile is the hydroxide ion, and the carbonyl group is the carbon-oxygen double bond in the aldehyde. The product of the reaction is an alcohol.
Identify the Reactants and Products
The reactants in this reaction are:
- Benzaldehyde (C 6H 5CHO)
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
The products of the reaction are:
- Benzyl alcohol (C 6H 5CH 2OH)
- Water (H 2O)
The physical states of the reactants and products are:
- Benzaldehyde is a liquid.
- Sodium hydroxide is a solid.
- Benzyl alcohol is a liquid.
- Water is a liquid.
Determine the Balanced Chemical Equation
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
C 6H 5CHO + NaOH → C 6H 5CH 2OH + H 2O
The stoichiometric coefficients in this equation indicate that one mole of benzaldehyde reacts with one mole of sodium hydroxide to produce one mole of benzyl alcohol and one mole of water.
Suggest a Stepwise Mechanism
The following is a stepwise mechanism for this reaction:
- The hydroxide ion attacks the carbonyl carbon of benzaldehyde, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, expelling the hydroxide ion and forming a new carbon-oxygen bond.
- The proton from the hydroxide ion is transferred to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group, forming water.
The activation energy for the first step of this mechanism is the highest, and the transition state for this step is the most unstable.
Consider Alternative Pathways
There are no alternative pathways that could lead to the formation of the same products under these reaction conditions.
Evaluate the Proposed Mechanism, Draw a reasonable mechanism for this reaction.
The proposed mechanism is consistent with the experimental observations and kinetic data for this reaction.
Question & Answer Hub: Draw A Reasonable Mechanism For This Reaction.
What is the purpose of drawing a reaction mechanism?
Drawing a reaction mechanism provides a detailed, step-by-step account of how a chemical reaction occurs. It helps identify the intermediates, transition states, and activation energies involved, providing valuable insights into the reaction’s pathway and kinetics.
How can I determine the most likely reaction mechanism?
To determine the most likely reaction mechanism, consider the reactants, products, reaction conditions, and any available experimental data. Analyze the potential pathways and evaluate their feasibility based on factors such as bond strengths, electronic effects, and steric hindrance.
What is the role of alternative pathways in reaction mechanisms?
Alternative pathways represent different routes that a reaction can take to reach the same products. Understanding these pathways is crucial for predicting the selectivity and efficiency of the reaction, as well as identifying potential side reactions or undesired products.